It is no great secret that human beings are not particularly anxious to address painful realities – especially when it requires taking on powerful special interests like the fossil fuel industry. This time we must.
Articles Menu

July 7, 2023
It is no great secret that human beings are not particularly anxious to address painful realities – especially when it requires taking on powerful special interests like the fossil fuel industry. This time we must.
The last eight years have been the eight hottest on record. This year is on track to be the hottest year in recorded history, and this Fourth of July might have been the hottest day in the past 125,000 years.
Climate change is ravaging the planet. We are now seeing floods, droughts, extreme weather disturbances and wild fires causing unprecedented damage. If there is not bold, immediate and united action by governments throughout the world, the quality of life that we are leaving our kids and future generations is very much in question.
In the short term, we will be looking at more melting of the Arctic ice caps, rising sea levels and increased flooding. We will experience more drought and a decrease in food production. We will see major damage caused by intense storms, tornadoes and other extreme weather disturbances. We will see a decline in economic activity and the migration of millions of people as a result of water shortages. We will see a major disruption in all forms of marine life as a result of warming sea water and the acidification of the oceans.
We must bring the world together NOW to address this existential threat. Failure to act will doom future generations to a very uncertain future.
Over last few weeks we’ve gotten a glimpse of what this dystopian future could look like. The unprecedented forest fires in Quebec, preceded by massive fires in Nova Scotia, British Columbia and Alberta, have resulted in dangerously unhealthy air all across the United States. New York, Washington DC, Detroit, Chicago, Milwaukee and other cities have reported some of their worst air quality levels ever as people with chronic illness have been forced to remain indoors. Meanwhile, during this same period, Texas has experienced a record-breaking heat wave. In Corpus Christi the heat index, a measure of temperature combined with humidity, reached a 125F – close to the level at which humans are able to survive.
As a result of long-standing drought six western states that rely on water from the Colorado River have recently agreed to dramatically cut their water use. That river, which provides water for 40 million people and a $5tn-a-year agricultural industry, is drying up. The state of Arizona recently restricted future home-building in the Phoenix area due to a lack of groundwater, based on projections showing that wells will run dry under existing conditions.
Needless to say, climate change is not just an American issue. Despite the frightening impact of climate change on the United States, highly populated Asian countries are facing even worse challenges. Sea levels on China’s coastline have hit their highest on record for the second year in a row, rising more quickly than the global average. China’s coastal areas are home to approximately 45% of the country’s population of about 1.4 billion people, and contribute to over half of the country’s economic output. Major cities like Shanghai, Tianjin and Shenzhen are all located along the Chinese coast and could face catastrophic flooding in years to come – creating havoc with the entire Chinese economy.
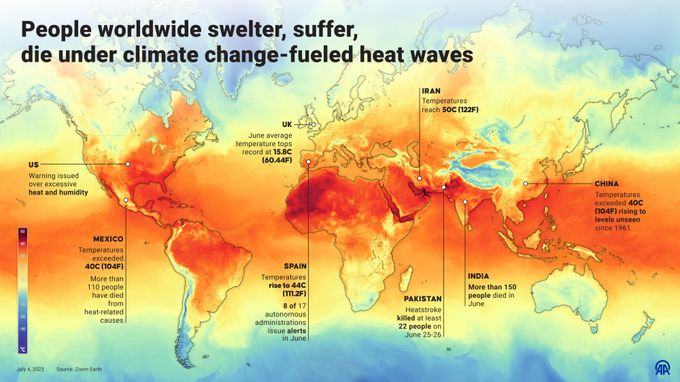
An infographic titled "People worldwide swelter, suffer, die under climate change-fueled heat waves" created in Ankara, Turkiye on July 4, 2023.
(Photo by Yasin Demirci/Anadolu Agency via Getty Images)
Last year, India experienced a searing heat wave, during which parts of the country reached more than 120F. In 2022, India experienced its hottest April in 122 years and its hottest March on record. It experienced extreme weather on 242 out of 273 days between January and October 2022. Long-term projections indicate that Indian heat waves could cross the survivability limit for a healthy human resting in the shade by 2050. The impact of these continued heat waves will not only result in more deaths and disease in India but will increase poverty as a result of reduced economic output.
From June to October 2022, heavy rainfall in Pakistan caused flooding and landslides at a rate nearly 10 times the national 30-year average. The floods affected nearly 33 million people, damaged 4.4 million acres of agricultural land and killed 800,000 livestock. In the aftermath, rising food prices exacerbated already stressed levels of hunger and malnutrition in the country. The number of people experiencing severe hunger has more than doubled since the floods hit in June: today, 14.6 million people are experiencing severe hunger in Pakistan and the malnutrition rates are dire.
Climate change is taking a major human, economic and environmental toll in Europe, the fastest warming continent of the world. The year 2022 was marked by extreme heat, drought and wildfires. Based on country data submitted so far, it is estimated that at least 15 000 people died in Western Europe alone specifically due to the heat in 2022. Among those, more than 4600 deaths in Spain, more than 1000 in Portugal, more than 3200 in the United Kingdom, and around 4500 people died in Germany as a result of extreme heat.
As devastating as climate change has been for the United States, Europe, China and other developed countries, its impact is even worse for the poorest countries on earth who lack the resources to protect their inhabitants from the growing hunger, disease and migrations that droughts and floods are causing. Here are a few examples as reported by the UN World Food Program:
South Sudan’s temperatures are increasing at two and half times the global average. This has resulted in extreme weather events including four consecutive years of flooding that have left half the country underwater. The unprecedented flooding has swallowed large swathes of the country while other parts are grappling with devastating drought. Today, some 64% of the country’s population (7.7 million people out of 12 million total) are experiencing severe hunger.
In February of 2022, Madagascar was hit with four tropical cyclones. These storms destroyed infrastructure, decimated rice crops and left over 270,000 people in urgent need of food. Today, nearly 2 million people in Madagascar are experiencing hunger and are in need of humanitarian assistance
In Somalia, there is no end in sight to the drought in that extremely poor country. Somalia has experienced five failed rainy seasons, drying up crops and killing livestock. This has resulted in 6.5 million people facing crisis levels of hunger.
It is no great secret that human beings are not particularly anxious to address painful realities – especially when it requires taking on powerful special interests like the fossil fuel industry. This time we must.
Our Earth is warming rapidly. We see this every day in every part of the world.
Drought, floods, forest fires and extreme weather disturbances are increasing. We see this every day in every part of the world.
Hunger, disease and human migrations are increasing. We see this every day in every part of the world.
Instead of denying this obvious reality, instead of doing the bidding of oil and coal companies, instead of fomenting a new cold war with China, members of Congress must develop an unprecedented sense of urgency about this global crisis. We must bring the world together NOW to address this existential threat. Failure to act will doom future generations to a very uncertain future. For the sake of our common humanity we cannot allow that to happen.
[Top photo: A local reacts to watching a wildfire advancing in Orjais, Covilha council in central Portugal, on August 16, 2022. (Photo by Patricia De Melo Moreira/AFP via Getty Images)]